Bloqueur de roue
Wheel chocks (or chocks) are wedges of sturdy material placed closely against a vehicle's wheels to prevent accidental movement. Chocks are placed for safety in addition to setting the brakes. The bottom surface is sometimes coated in rubber to enhance grip with the ground. For ease of removal, a rope may be tied to the chock or a set of two chocks. One edge of the wedge has a concave profile to contour to the wheel and increase the force necessary to overrun the chock. Most commonly, chocks are seen on aircraft and train cars.
Automobiles usually have parking brakes on the rear wheels. If the rear axle is jacked off the ground with only the parking brake set, the vehicle may roll on the front wheels and fall. Chocking the front wheels prevents this mishap.
Motorcycle and bicycle chocks are bifurcated and fit around the wheel, supporting the bike and preventing its movement.
The mining industry uses wheel chocks to protect lubrication trucks and heavy maintenance vehicles from slipping on off-road terrain when placed in Park. The huge haul trucks, which can weigh up to 450 tonnes, require a much larger wheel chock that itself will weigh almost 40 kilograms. These circumstances will benefit from urethane wheel chocks that are lightweight enough to be maneuvered, yet can withstand the responsibility of holding a truck if a brake should fail. The Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) has established standards that wheel chocks are used when a vehicle is parked on a grade, and OSHA has guidelines that require wheel chocks during loading or unloading of a heavy truck.
Read more on Wikipedia
Cet outil est utilisé dans
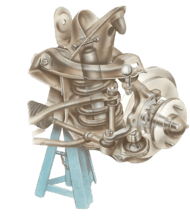
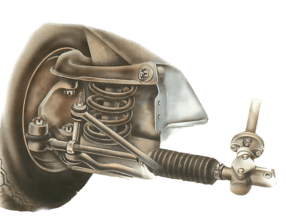
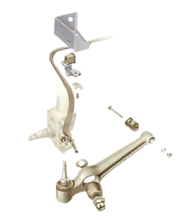
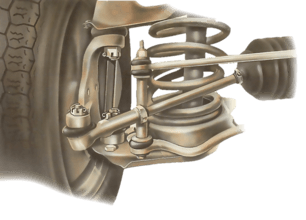
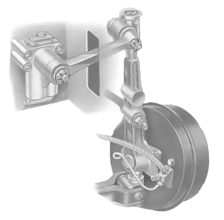
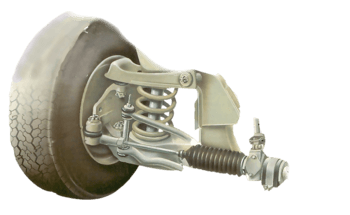
Driven wheels - independent suspension Cars with front-wheel drive have front-wheel bearings that...
Brake fluid is generally renewed when a leaking or sticking wheel cylinder on a drum brake is re...
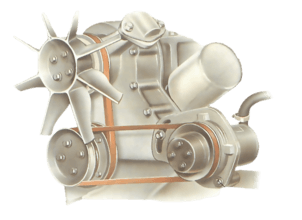
If the oil pump is fitted to the outside of the engine, you may be able to reach it...
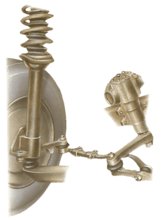
If you have to replace a coil spring on the front suspension, the replacement spring must be of ...
Part of a steering rack check involves raising the front of the car but retaining its weight on ...
Modern telescopic dampers cannot be overhauled at home. The only servicing possible is to replac...
The forces imposed on the anti-roll bar subject it to constant twisting and flexing, which in tu...
Track-rod-end ball joints are not adjustable on later cars. If they wear, you must replace them....
Any fuel leak, however small, can cause a fire. Do not drive a car with a suspected leak until yo...
Either or both of the upper and lower swivels may have grease nipples; ball joints have them on ...
Tyres are put under tremendous strains when a car is being driven. There are only four relativel...
Front lever-arm damper A lever-arm damper on the front often acts as part of the suspension unit....
A steering box check involves raising the front of the car but keeping its weight on the wheels,...
Places where vital components are mounted on the bodywork or chassis should be inspected at leas...
La courroie qui entraîne une pompe de fluide hydraulique de direction est assistée généralement ...
The clutch cable has a steel-wire inner core sliding inside an outer sheath. It should last at l...
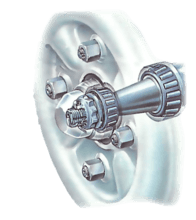
Wheel bearings need periodic checking - and adjusting if necessary - usually at 12,000 mile serv...
When you take the wheels off to inspect the tyre walls, clean the wheels thoroughly and look clo...
Steering swivel pins may wear out after a high mileage (60,000 plus), or sooner if they have not...
Most modern cars have sealed for life joints in at least part of the steering system. These do no...
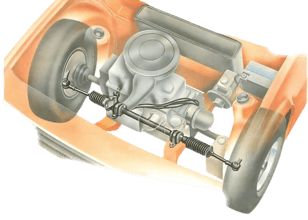
Most modern cars have rack-and-pinion steering gear, mounted across the car. Usually the rack ho...
If testing the starter circuit (See Checking the starter circuit) indicates a fault in the starte...